What is Spondylolysis?
Spondylolysis is a cause of back pain in young people. It is known as a 'stress' fracture, and like many sports stress fractures, it usually heals to become symptom-free.
Who is Affected by Spondylolysis?
The diagnosis of a spondylolysis should be considered in back pain that occurs after strenuous sports on a consistent basis. Young gymnasts and young athletes involved in 'throwing' sports are most commonly affected. On the positive side, it seems more common in elite athletes.
Causes of Spondylolysis
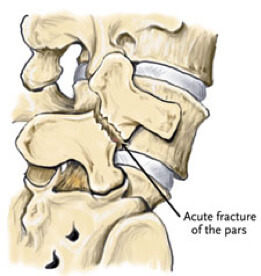
It is a stress fracture that occurs at the 'pars interarticularis', which is a part of the back of the spinal bone, or the neural arch. It is not a serious structural fracture, and so normal activities can continue.